새로운 연구에 따르면, 달 궤도의 '흔들림'이 2030년대에
기록적인 홍수를 일으킬 수 있다고 한다.
By Brandon Specktor - Senior Writer about 4 hours ago
약 4시간 전 선임 작가 - 브랜든 스펙터
The entire US coastline is in for a one-two punch from the lunar cycle and climate change.
미국의 전체 해안선은 달의 순환과 기후 변화로 인해 원투
펀치를 맞을 것이다.
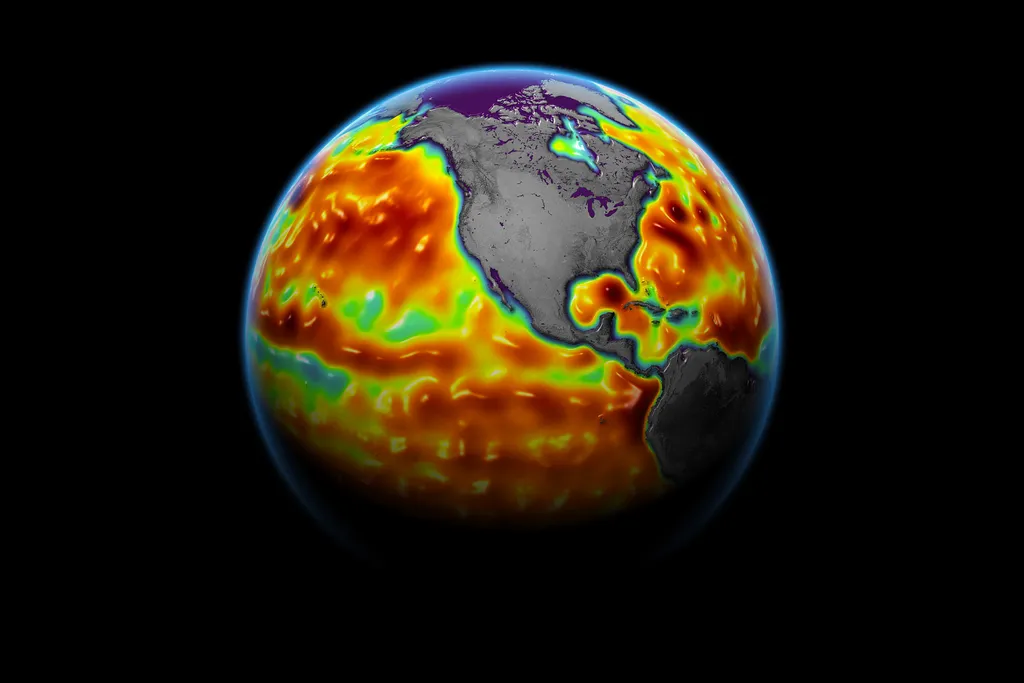
A map showing sea surface height anomalies in June 2021, with ares in red and orange representing sea levels 10 to 15 cm higher than normal. (Image credit: NASA Earth Observatory/ Joshua Stevens)
2021년 6월 해수면 높이 이상을 나타낸 지도로, 적색과 주황색은
정상보다 10~15cm 높은 해수면을 나타낸다.
(이미지 크레딧: 나사 지구 관측소/조슈아 스티븐스)
Climate change has already increased the frequency and severity of hurricanes and other extreme weather events around the world. — But there's a smaller, less splashy threat on the horizon that could wreak havoc on America's coasts.
기후 변화는 이미 허리케인과 전 세계의 다른 극한 기후 사건의
빈도와 심각성을 증가시켰다.
— 하지만 미국 연안에 대혼란을 일으킬 수 있는, 더 작고 덜 번지는
위협이 지평선 상에 있다.
High-tide floods, also called "nuisance floods," occur in coastal areas when tides reach about 2 feet (0.6 meters) above the daily average high tide and begin to flood onto streets or seep through storm drains. True to their nickname, these floods are more of a nuisance than an outright calamity, inundating streets and homes, forcing businesses to close and causing cesspools to overflow — but the longer they last, the more damage they can do.
"방해 홍수"라고도 불리는 고조 홍수는 조수가 하루 평균 만조보다
약 2피트(0.6미터) 위에 도달하고 거리로 넘쳐나거나 폭풍의 배수구를
통해 스며들 때 해안 지역에서 발생한다.
그들의 별명대로, 이러한 홍수는 완전한 재앙이라기 보다는 성가신
일이고, 거리와 주택이 범람하고, 기업들이 문을 닫게 하고 쓰레기
웅덩이가 넘쳐나게 만든다. 하지만 홍수가 오래 갈수록 더 많은
피해를 입힐 수 있다.
The U.S. experienced more than 600 of these floods in 2019, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). But now, a new study led by NASA warns that nuisance floods will become a much more frequent occurrence in the U.S. as soon as the 2030s, with a majority of the U.S. coastline expected to see three to four times as many high-tide flood days each year for at least a decade.
국립해양대기청 (NOAA)에 따르면 미국은 2019년에 이러한 홍수를
600번 이상 겪었다.
하지만 이제, NASA가 주도하는 새로운 연구는 적어도 10년 동안
매년 3~4배의 높은 조수의 홍수를 볼 것으로 예상되는 미국 해안선의
대다수와 더불어 2030년대에 미국에서 성가신 홍수가 훨씬 더 자주
일어날 것이라고 경고하고 있다.
The study, published June 21 in the journal Nature Climate Change, warns that these extra flood days won't be spread out evenly over the year, but are likely to cluster together over the span of just a few months; coastal areas that now face just two or three floods a month may soon face a dozen or more.
이 연구는 6월 21일 학술지 '네이처 기후 변화'에 실렸으며, 이번 추가
홍수일은 1년 내내 고르게 퍼지지 않을 거라고 경고하지만, 단 몇 개월
에 걸쳐 함께 뭉쳐질 가능성이 높으므로 이제 한 달에 두세 번 홍수에
직면하는 해안 지역은 곧 십여 개 이상의 홍수에 직면할 수도 있다.
These prolonged coastal flood seasons will cause major disruptions to lives and livelihoods if communities don't start planning for them now, the researchers cautioned.
이렇게 장기화된 해안 홍수 계절은 지역 사회가 지금 당장 계획을 세우지
않는다면 생활과 생계에 큰 지장을 줄 것이라고 연구원들은 경고했다.
"It's the accumulated effect over time that will have an impact," lead study author Phil Thompson, an assistant professor at the University of Hawaii, said in a statement. "If it floods 10 or 15 times a month, a business can't keep operating with its parking lot under water. People lose their jobs because they can't get to work. Seeping cesspools become a public health issue."
"시간이 지남에 따라 누적된 효과가 영향을 미칠 것입니다,"라고 하와이
대학의 필 톰슨 조교수는 성명에서 말했다.
"한 달에 10~15번 정도 홍수가 나면 사업체는 주차장이 물에 잠겨 작동
을 유지해갈 수 없습니다. 사람들은 일하러 갈 수 없기 때문에 직장을
잃습니다. 오물 웅덩이가 범람하는 것은 공중 보건 문제가 됩니다."
Several factors drive this predicted increase in flood days.
몇 가지 요인들이 홍수일의 이러한 예상 증가를 주도하고 있다.
For one, there's sea level rise. As global warming heats up the atmosphere, glacial ice is melting at a record pace, dumping enormous amounts of meltwater into the ocean. As a result, global average sea levels have risen about 8 to 9 inches (21 to 24 centimeters) since 1880, with about a third of that occurring in just the last 25 years, according to NOAA. By the year 2100, sea levels could rise anywhere from 12 inches (0.3 m) to 8.2 feet (2.5 m) above where they were in 2000, depending on how well humans restrict greenhouse gas emissions in the coming decades.
우선 해수면이 상승한다. 지구 온난화가 대기를 뜨겁게 달구면서, 빙하가
기록적인 속도로 녹으면서 엄청난 양의 녹은 물을 바다에 버리고 있다.
그 결과, NOAA에 따르면, 1880년 이후 지구 평균 해수면이 약 8에서 9인치
상승했고, 그 중 약 1/3이 지난 25년 사이에 발생했다고 한다.
2100년까지, 전체 해수면은 인간이 앞으로 수십 년 동안 온실 가스 배출을
얼마나 잘 제한하느냐에 따라 2000년에 비해 12인치(0.3미터)에서 8.2피트
(2.5미터)까지 상승할 수 있다.
While rising sea levels alone will increase the frequency of high-tide floods, they will have a little help from the cosmos — specifically, the moon.
해수면이 상승하는 것 만으로도 높은 조수의 홍수의 빈도를 증가시킬 수
있지만, 우주, 특히 달로부터 약간의 도움을 받을 수 있을 것이다.
The moon influences the tides, but the power of the moon's pull isn't equal from year to year; the moon actually has a "wobble" in its orbit, slightly altering its position relative to Earth on a rhythmic 18.6-year cycle. For half of the cycle, the moon suppresses tides on Earth, resulting in lower high tides and higher low tides. For the other half of the cycle, tides are amplified, with higher high tides and lower low tides, according to NASA.
달은 조수에 영향을 미치지만, 달의 끌어당기는 힘이 해마다 같지 않다.
달은 실제로 궤도에 율동적인 18.6년 주기 동안 지구에 대한 위치를
약간 바꾸면서 그것의 궤도에서의 "흔들림"이 있다.
이 주기의 절반 동안, 달은 지구의 조수를 억제하여 더 낮은 고조수와
더 높은 저조수를 초래한다.
NASA에 따르면, 그 주기의 나머지 절반의 조수는 더 높은 고조수와 더
낮은 저조수와 더불어 증폭된다.
We are currently in the tide-amplifying part of the cycle; the next tide-amplifying cycle begins in the mid-2030s; — and, by then, global sea levels will have risen enough to make those higher-than-normal high tides particularly troublesome, the researchers found.
우리는 현재 조수 증가 주기의 일부에 있으며, 다음 조수 증가 주기는
2030년대 중반에 시작되며, 그리고 그때쯤에는 지구 해수면이 정상보다
높은 조수를 특히 골치 아프게 만들 정도로 충분히 상승할 것이다, 라는
사실을 연구원들은 발견했다.
Through the combined effect of sea-level rise and the lunar cycle, high-tide flooding will increase rapidly across the entire U.S. coast, the team wrote. In a little more than a decade, high-tide flooding will transition "from a regional issue to a national issue with a majority of U.S. coastlines being affected," the authors wrote. Other elements of the climate cycle, like El Niño events, will cause these flood days to cluster in certain parts of the year, resulting in entire months of unrelenting coastal flooding.
해수면 상승과 달 주기의 복합적인 영향을 통해, 높은 조수의 홍수는
미국 해안 전체에서 빠르게 증가할 것이라고 연구팀은 썼다.
저자들은 10년이 조금 넘으면 "대부분의 미국 해안선이 영향을 받는
지역적 문제에서 국가적 문제로" 전환될 것이라고 썼다.
엘니뇨 이벤트와 같은 다른 기후 주기 요소는 이러한 홍수일을 연중
특정 부분에 집결시켜 수개월 동안 지속되는 해안 홍수를 초래할 것이다.
Scary as this pattern sounds, it is also important to understand for planning purposes, the authors wrote.
이 패턴이 무섭게 들린다고 저자들은 말했다. 목적 계획을 위해 이해하는
것 또한 중요하다고 저자들은 썼다.
"Understanding that all your events are clustered in a particular month, or you might have more severe flooding in the second half of a year than the first — that's useful information," study co-author Ben Hamlington of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory said in the statement.
NASA 제트추진연구소의 연구논문 공동저자인 벤 햄링톤은 성명에서
"여러분의 모든 사건들이 특정 달에 집중되어 있거나 1년 전보다 하반기에
더 심각한 홍수가 발생할 수 있다는 것을 이해하는 것은 유용한 정보입니다,"
라고 말했다.
Extreme weather events may get all the national media attention as they batter America's coasts, but high-tide flooding will soon be impossible to ignore. Best to start planning for it now, before it's too late, the authors concluded.
극단적인 기상 이벤트가 미국 해안을 강타하기 때문에 모든 전국 언론의
관심을 받을 수 있지만, 곧 높은 조수의 홍수는 무시할 수 없을 것이다.
너무 늦기 전에 지금 계획을 시작하는 것이 가장 좋다고 저자들은 결론을
내렸다.
Originally published on Live Science.
라이브 사이언스에 원본으로 발간됨.

댓글 없음:
댓글 쓰기